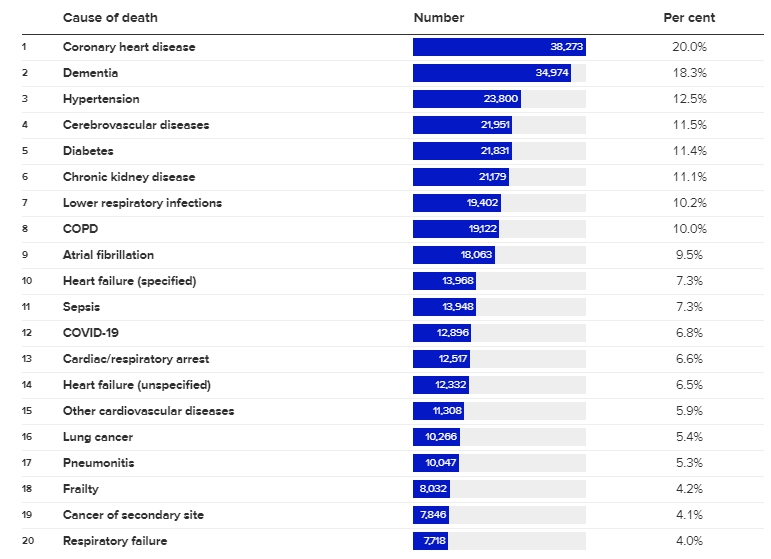
This report highlights a critical issue in Australia’s public health landscape, emphasizing the predominant role of chronic conditions such as coronary heart disease and dementia in mortality rates. The insight that multiple causes contribute to four out of every five deaths underscores the complexity of health issues leading to mortality and the importance of multifaceted public health strategies. It points to the necessity of addressing lifestyle factors and comorbid conditions that can exacerbate or trigger fatal outcomes.
Coronary heart disease’s prominence as a leading cause of death is consistent with global trends, where heart disease often tops the list of mortality causes. The close following of dementia, including Alzheimer’s disease, reflects the aging population and the increasing prevalence of these conditions, highlighting the need for robust healthcare systems capable of managing chronic illnesses and supporting an aging population.
High blood pressure, cerebrovascular diseases, and diabetes are also major contributors to mortality in Australia, as reported by the AIHW. These conditions, often linked to lifestyle factors such as diet, physical inactivity, and smoking, underline the significance of preventive health measures and public health campaigns aimed at encouraging healthier lifestyles to reduce the risk of these diseases.
Lower respiratory infections, cardiac/respiratory arrest, and sepsis being the most common direct causes of death point to the acute events that ultimately lead to mortality in individuals with underlying conditions. It suggests that while chronic conditions significantly affect longevity and quality of life, it is often an acute exacerbation or complication that directly leads to death.
The AIHW’s approach of considering all factors listed on death certificates provides a more comprehensive understanding of mortality and its causes. This method acknowledges the complexity of health and mortality and the often interconnected factors that contribute to a person’s death. It underscores the need for a holistic approach to healthcare and public health policy, focusing not only on treatment but also on prevention, early detection, and management of chronic diseases.
Public health initiatives aimed at addressing the root causes and contributors to these leading causes of death, such as smoking cessation programs, nutritional education, physical activity promotion, and mental health support, are vital. Additionally, improving healthcare access and quality, particularly for elderly populations and those at high risk of chronic conditions, could play a significant role in reducing mortality rates related to these diseases.
The findings from the AIHY report serve as a call to action for policymakers, healthcare professionals, and the public to intensify efforts in combating the leading causes of death through comprehensive and integrated public health strategies. By targeting the root causes and providing adequate support for those living with chronic conditions, Australia can work towards reducing the burden of these diseases and improving the health and well-being of its population.